Accelerating Pulp and Paper Processing with Advanced Process Control
Innovative pulp and paper operators are turning advanced process control, automated testing, and quality control system data into actionable business insights that improve operational efficiency all along the value chain.
Automation and control technologies continue to revolutionize process industries worldwide, and the pulp processing and paper-making sector is no exception. Digital innovations like artificial intelligence (AI), the industrial internet of things (IIoT), and advanced data analytics are transforming the entire pulp and paper (P&P) value chain: from woodyard to shipment, from mill to enterprise.
Armed with digital tools from a trusted technology provider, P&P operators now have visualization and control of every facet of their operations, enabling them to make more informed, data-driven decisions that improve scheduling, quality control, and efficiency, reduce downtime, raw material usage, energy consumption, and waste, ultimately helping to deliver world-class business results.
Successful digital innovators are already witnessing throughput gains of 5 to 10%, yield gains of up to 5 percentage points, as well as significant savings on materials, chemicals and energy. For the industry, this represents a $4 to $6 bn opportunity, one that companies cannot afford to miss.
However, it’s widely reported that companies are not harnessing the true potential of their manufacturing data, with more than two-thirds often going unused for analytics. Findings from IBM Research estimate that, while it is collected by organizations, as much as 88% of IIoT data goes unused.
As digitalization progresses, it brings a free flow of data from both information technology (IT) and operational technology (OT) applications across the value chain, making interoperability a priority.
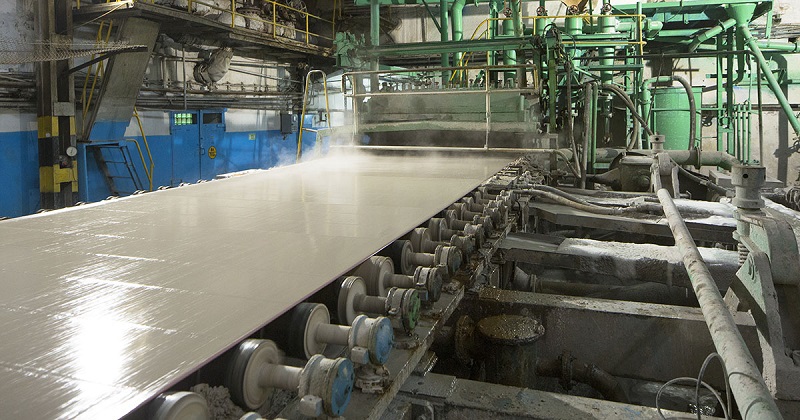

Figure 1. Controls used for pulp and paper industries include a wide array of process sensing, thermal and mechanical outputs, and data collection. Image used courtesy of ABB
In this article, we will examine advanced process control (APC), automated paper testing, and quality control systems (QCS) and their applications across a range of P&P processes, highlighting advancements, benefits, and challenges on the journey towards more efficient, sustainable, and high-quality paper production.
Advanced Process Control (APC) and its Multiple Applications
Like all industrial operators, P&P mills are advised to ask themselves the following question: what do we want this technology to do for our business? If the answer is to help ensure on-spec paper at the lowest cost, then investing in the latest QCS makes solid business sense.
When it comes to gaining valuable business insights from data, many connected digital solutions, such as ABB Ability, offer multiple applications for pulp and paper through world-leading distributed control systems (DCS), including the System 800xA as the automation layer, and both QCS solutions and APC where appropriate to the application.
The operational benefits of APC for pulp mills include stabilizing and improving process operations, and minimizing the variation of key conditions while considering process constraints. These benefits translate into financial gains due to increased throughput and minimized energy and raw material consumption, helping producers hit their key performance indicators by increasing throughput and reducing energy use.
APC for pulp mills provides monitoring, predictive analytics, and closed-loop process control to optimize mill operations. The solution stabilizes the process, reduces chemical use, and coordinates the numerous loops to ensure optimum product quality at minimum variance. APC and its related process modeling are of particular value in the P&P space, where many of the processes are notoriously difficult to measure.
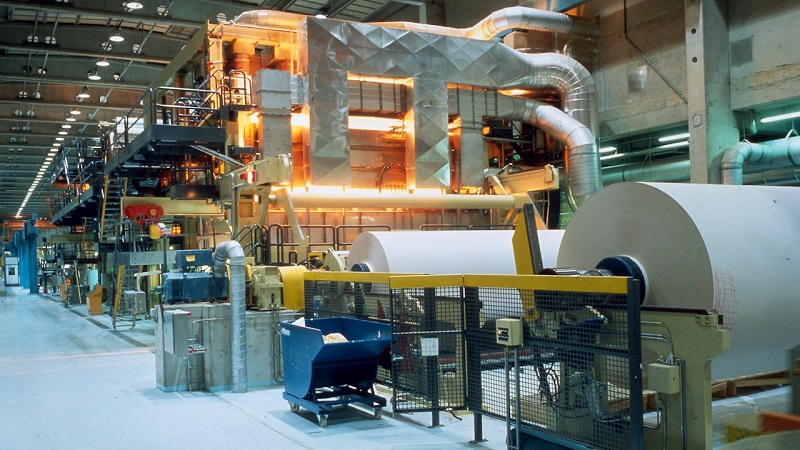
Figure 2. Motors and drives are used across many lines of products including pulp, paper, and consumer packaging products. Image used courtesy of ABB
Let’s take the real-world example of a pulp plant in Europe to illustrate how APC can be used to optimize the operation of mills, in this instance centering on the lime kiln. Here, the application of ABB Ability APC resulted in a 58% reduction in cold end temperature, a 26% reduction in oxygen, energy consumption savings of 5.02%, and a 62% reduction in residual carbonate variation.
APC also encompasses model predictive control (MPC), whereby a linear or non-linear mathematical model of the process and optimization algorithms are used to estimate unmeasured states and control process variables. MPC for P&P mills includes nonlinear mathematical models to describe the process, and the design of a suitable cost function that considers the goals to achieve.
In addition to MPC, the latest technologies, ranging from data access to analytics and visualization, are leveraged in APC to help customers optimize operations and hit their key targets.
Automated Paper Testing for Rapid, Accurate Results
Manually gathering and testing paper samples is laborious and time-consuming, and can result in inaccuracies. Automated paper testing systems address such challenges by reducing measurement uncertainty or test variability, delivering both accurate and repeatable quality reports in minutes.
This is another example of how automation and digital solutions empower mill operators to make more informed, data-driven decisions and take quicker corrective action, allowing paper or board makers to shift production targets and achieve more consistent performance leading to higher profits.
Systems like ABB's L&W Autoline handle everything from sample preparation to the final reel report with minimal operator involvement to provide quick and accurate measurement and reporting of key paper properties for better efficiency, freeing up personnel to focus more on quality optimization.
Moving from manual to automated testing is an important stage in a P&P operator’s digital journey. Mills can run more tests, with hundreds and thousands of data points simultaneously, with a higher level of consistency and more detailed profiles of the sheet across the whole width of the paper.
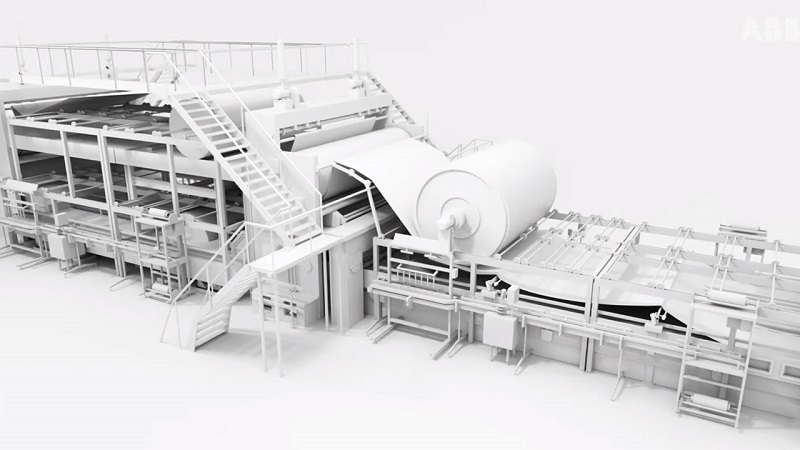
Figure 3. Digitization is important for pulp and paper, as with any industry, for resilience and the ability to meet future demands. Image used courtesy of ABB
A Question of Quality
QCS solutions give mills complete visibility over process and system performance, enabling them to identify and fix issues along the length of the machine (stock preparation, wet end, pressing, drying, coating, finishing, etc) using integrated online measurement and process quality controls.
QCS for pulp and paper integrates quality control and measurement, control systems, and mill management to evaluate quality throughout the entire manufacturing process. Mills can inspect the product web with consistent and repeatable results, correct quality issues quicker, and increase product output by reducing sheet breaks and optimizing runnability.
In conclusion, there are major opportunities for the P&P sector to benefit from digital technologies to bridge the gap that has traditionally existed between IT and OT. By applying data analytics, AI, and machine learning to the growing volume of available production data, producers now have the power to transform the resulting improved visibility into actionable business insights to improve operational efficiency all along the value chain, culminating in better products and profitability.

 Facebook
Facebook Google
Google GitHub
GitHub Linkedin
Linkedin








