AES Eases Solar Panel Installation with 6-Axis and Mobile Robotics
AES doubles down on solar panel installation with Maximo, a robotic system that uses AI-powered vision and continuous learning to optimize the placement and connection of solar panels in the field.
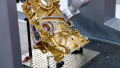
The AES Corporation, a global leader in grid and alternative energy solutions, has recently developed Maximo, a robotic system that uses a combination of mobile and articulated technologies along with AI-powered software to work alongside human workers in placing and attaching solar panel modules.
Solar Panels In Demand
It’s no secret that the world demands more energy on a continual basis, and solar panels are poised to quickly supply some of this required energy. Installing solar panels can require many hours or even days of heavy lifting and manual input. Not only are they heavy, but they require detailed, attentive wiring skills, and proper placement is key.
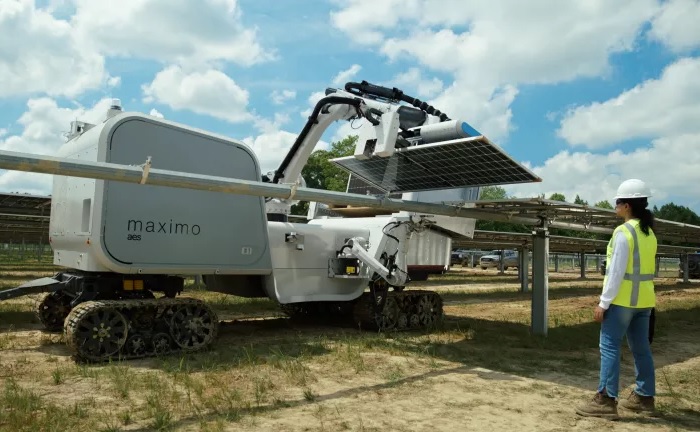

Maximio, the new robot created by AES for the installation of solar modules. Image used courtesy of AES
Solar Robot: Maximo
The heavy weight of solar panels presents a logistical challenge, especially when dealing with large-wattage panels. Proper ground placement is pivotal to future performance and reliability. Maximo uses AI-powered computer vision systems to locate positions and connect solar modules accurately. This reduces the heavy lifting that workers would have to perform, thus increasing safety and accelerating the installation process.
The Maximo system also uses continuous machine learning to optimize installation and adapt to changing environments. With ever-varying light conditions of an outdoor environment, AES needed to ensure the Maximo could work without problematic variations, so a proprietary AI image processing system was created that would reconstruct images obscured by glare or other lighting conditions.
A common argument against the employment of robotics is a replacement of human workers in the field, but in this case, the result is quite the opposite. With Maximo being able to scale up the installation of these solar fields, project timelines are accelerated, and new high-tech, high-paying jobs are created. Someone needs to program Maximo and repair the systems when they break down. It also gives technicians an opportunity to develop AI skills they might not have otherwise gained.
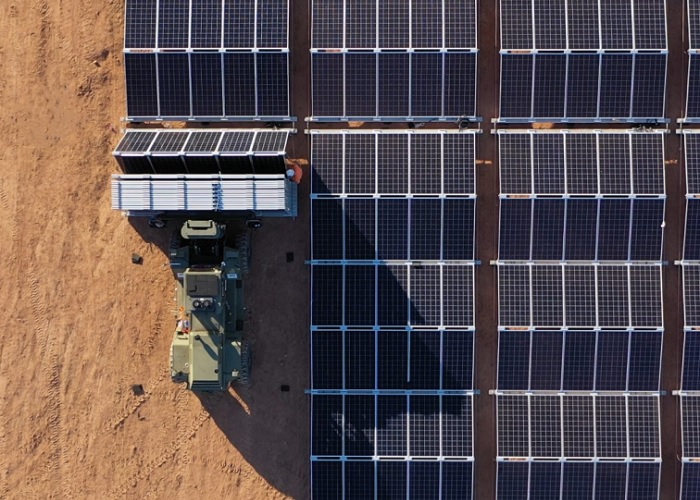

A robot installs an array of solar modules. Image used courtesy of AES
Already Working in the Field
Maximo has already been field-tested by AES, providing installation support for nearly 10 MW worth of solar modules. Over the next three years, AES will use Maximo to install over 5 GW of solar modules. Maximo is currently scheduled to install 2 GW at the Bellefield project in Kern County, California, a project in contract with Amazon.
With companies trying to achieve net-zero carbon emissions, the solar panel installation industry needs to scale accordingly. Even AES is stating that by 2050 they plan to be net zero carbon emissions for their entire business portfolio.
Technology’s Drive for Energy
What’s driving this increasing demand for energy?
Data centers, electric vehicles, AI programs, online data storage, and the list goes on... All of these technologies require energy, and as our desire to use advanced, modern devices grows, so does the demand for the energy necessary to power them.
According to AES, the current solar market demands approximately 15,000 solar modules per hour, which is difficult to fulfill with traditional installation practices alone. By using reliable robotic devices and algorithms, AES hopes to reduce the installation time and more easily fulfill the energy demand for the future.
Featured image used courtesy of AES

 Facebook
Facebook Google
Google GitHub
GitHub Linkedin
Linkedin