Energy and Automation Join Forces: Robots and Solar Materials
The worlds of power and control engineering are collaborating to create a new research robot, scanning multiple materials to configure the most effective material alloy combinations for a more efficient energy future.
Without a doubt, energy production is one of the most crucial elements of modern infrastructure, but have you ever stopped to think about how the essential materials first arrive at solar, wind, or hydro facilities perfectly designed to optimize energy harvesting?
The first step in any manufacturing process involves the research and design of the best materials to accomplish a specific task. For many alternative energy-generating technologies like solar or wind, materials must be both strong and resilient enough to withstand terrific dynamic forces and extended exposure to the elements. Once material properties are well understood, the optimized formula can then be sourced in great enough quantities to introduce economies of scale and meet the current and future demands of utilities.
To better understand critical material properties and develop effective formulations faster, a research team at NC State University announced the creation of an automated robotic work cell solution named the RoboMapper. According to the developers, Robomapper was designed and engineered to accelerate the selection and analysis of materials and find the best formulations to boost energy yield, increase stability and extend operating life.
Robots in Research
Robots used for material development in the lab generally are generally similar to most common industrial robots. They must be fast, accurate, and capable of handling a wide array of tools to accomplish different tasks. However, material-assessing robots are likely to require fewer axes of motion like those seen in factories and warehouses. In this case, laboratories usually rely on SCARA or cartesian configured systems.
Many robotic lab tools are designed to replicate the workflows around a researcher, so the scale and footprint of most automation is human-centric. That means most data is obtained from samples that are on the order of centimeters or inches.
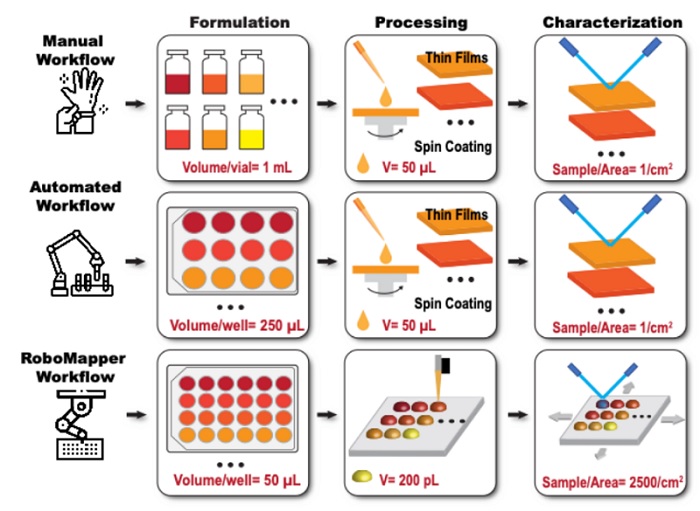
A comparison of manual and automated laboratory workflows. The final row illustrates how RoboMapper consolidates samples for greater efficiency. Image used courtesy of NCSU
NCSU’s RoboMapper
Professor Aram Amassian, leading the research team from NCSU, offered some insight into the strategy of the RoboMapper automated research process. “Similar information exists on volumes that are orders of magnitude smaller for the same materials. If modern robotics could make smaller samples and place them on a chip with higher density, and other tools could evaluate these materials with the same fidelity as traditional centimeter- and inch-scale samples, then there should be no fidelity lost in the data.”
Amassian also explained how the RoboMapper introduces a more efficient solution. “The RoboMapper is designed around this concept [of smaller sample sizes]; it leverages tech used in additive manufacturing: modern picoliter volume printing and micropositioning to achieve all of the small-scale data collection.”
As noted, RoboMapper is an automated robotic work cell rather than a single dedicated robot. One section of the cell performs the formulation work, while the other dispenses the formulated alloy, of which multiple samples can be prepared for testing at the same time. The final step is characterization, which includes a series of tests performed on the samples to record the data.
In this way, the RoboMapper is a combination of various linear axes of motion and end tools to replicate precise research work on a miniature scale, with the same integrity and fidelity of any traditional system.
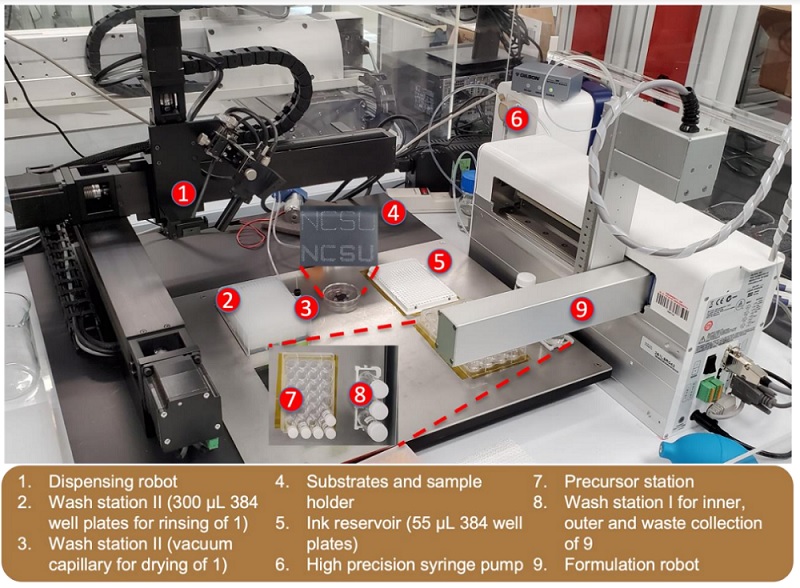
The labeled parts of the RoboMapper system show the consolidated approach to formulation and characterization. Image used courtesy of NCSU
Perovskite Materials
Material creation is a tricky task to automate because solar collection materials are crafted from the atomic level, with crystal structures and alloys mixed and set in the perfect arrays to collect light energy. The NCSU research team has paid particular attention to the category of materials called Perovskite.
This material category, commonly used for solar production, involves the bonding of two positive ions with a third negative ion, often an oxide. Many materials can be combined to create the ions, leading to an entire category of research to design the best materials that exhibit the needed qualities for high-efficiency photovoltaic operation.
For solar production specifically, the perovskite families most commonly investigated include ammonium and metal positive ions, along with iodine negative ions, formed into complex alloys. Some of these alloys have been shown to reach efficiencies above 25% with higher efficiencies possible. For photovoltaic cells, efficiencies above 30% would be considered quite an efficient high-yield material.
Initial Research Conclusions
While the RoboMapper remains poised to make great strides in the development of new perovskite alloys, there are some initial findings that are worthy of note. For example, Amassian mentioned that large-scale lab processes generate larger plastic and glass waste byproducts, and that through miniaturization and consolidation RoboMapper can reduce lab waste significantly.
Perhaps more important is the energy savings the automated, robotic system delivers with each analysis. Even though the energy required to accomplish its task is relatively minimal, energy is a costly resource that packs an environmental impact. As energy demands increase, so will the need for increased energy supply. Any process that introduces energy efficiency and reduces costs will likely receive a warm welcome by researchers and material scientists.
Research highlights and data from NCSU’s team demonstrate how innovation, engineering collaboration, and a combination of materials, mechanics, automation and controls, can work together to build and power a better future!

 Facebook
Facebook Google
Google GitHub
GitHub Linkedin
Linkedin