Relativity Space Continues Mission to 3D Print Rockets Using World’s Largest Industrial 3D Printers
Relativity Space, a private space company, gathered new investments for the development of 3D printed rockets.
The company is estimated to be worth 2.3 billion dollars with this latest round of funding.
Who is Relativity Space?
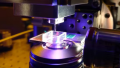
Relativity Space is a company that aims to pioneer its way into the future. The company relies on digital infrastructure and new industry techniques. Relativity’s most notable advancement is their use of Stargate. The Stargate is a large scale metal alloy 3D printer that promises to cut production time to a fraction of traditional methods.
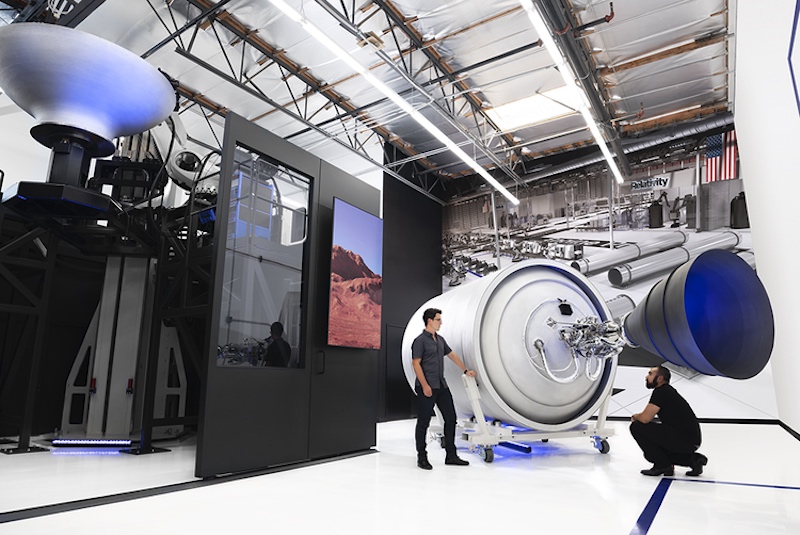

The Stargate 3D Printer. Image courtesy of Relativity Space.
Their mission to accelerate our space development and to help colonize Mars sooner than before is now one step closer.
War Chest Capital
Relativity announced a $500 million investment in their D series funding round. The investors include Tiger Global Management, Fidelity, Baillie Gifford, ICONIQ Capital, General Catalyst, XN Capital, Senator Investment Group, and Elad Gil.
Additionally, existing Relativity shareholders include Bond Capital, Tribe Capital, K5 Global, 3L Capital, Playground Global, Allen & Company, Mark Cuban, and Spencer Rascoff.
The Terran 1 rocket made using these methods will cost 12 million dollars to put into low earth orbit with a 1250 kg payload.
This is right around the cost used to put up SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket. Relativity has also moved its headquarters to a 120,000 square foot facility in Long Beach, California. Relativity will remain a private company.

Relativity's latest headquarters before they moved in. Image courtesy of Relativity Space.
“It lets us put our heads down and execute and not have to worry about some of the overhead of being a public company today,” said Tim Ellis, Co-founder & CEO at Relativity Space.
“We achieved that handily and are humbled by the level of interest from these world class investors,” Ellis noted.
Next-Generation Technology
Relativity uses AI-driven advanced digital techniques to produce their rocket parts. The Stargate Metal 3D printer uses laser metal sintering technology to create large scale cones, nozzles, and many other parts for a rocketship.
Relativity claims that their rockets use less than 1,000 parts with their capabilities compared to over 100,000 parts for a rocketship built with traditional manufacturing methods.
Relativity’s factory is software-driven with a simple supply chain that can create a project in two months with a six month iteration time. This can be compared to traditional methods at a 24 month build time and 48 month iteration time. Relativity shares a common goal with other private space companies. Relativity wants to make strides in the industry within ten years. They also want boots on Mars by that time too.
Relativity has set sights on the industrialization of Mars as well. Additive manufacturing in aeronautics and space has simplified processes and made interplanetary travel a more feasible goal that we will likely see in our lifetime.
Developing proprietary materials to use in additive manufacturing will hopefully cut down costs and production times and make the space industry far more sustainable.

 Facebook
Facebook Google
Google GitHub
GitHub Linkedin
Linkedin