Yokogawa OpreX: New Robot Solution for Plant Management Efficiency
Yokogawa has added to its OpreX software with a new application to help facilitate the use of robots in dangerous maintenance and inspection operations and in other vital plant processes.
Yokogawa, a company specializing in measurement, control, and information technology, has recently announced the development and release of OpreX™ Robot Management Core. The software application is an addition to Yokogawa’s OpreX Asset Management and Integrity family. Management Core has been designed to help plants automate some maintenance tasks previously performed by maintenance personnel.
The software also gives manufacturers access to plant control and safety data for Industry 4.0 applications. In addition, procedural instructions can be relayed through the system to the robots enabling a first-of-its-kind solution that moves end users closer in the direction of fully autonomous plant operation capabilities.
The Need For Automated Robotic Maintenance
The idea for the new system was developed as a response to the need for autonomous capabilities in high-risk areas, such as the oil and gas industries, and as a way to better automate the management of robotic tasks. In many industrial settings, there is a need to inspect and maintain systems that are hazardous to humans.

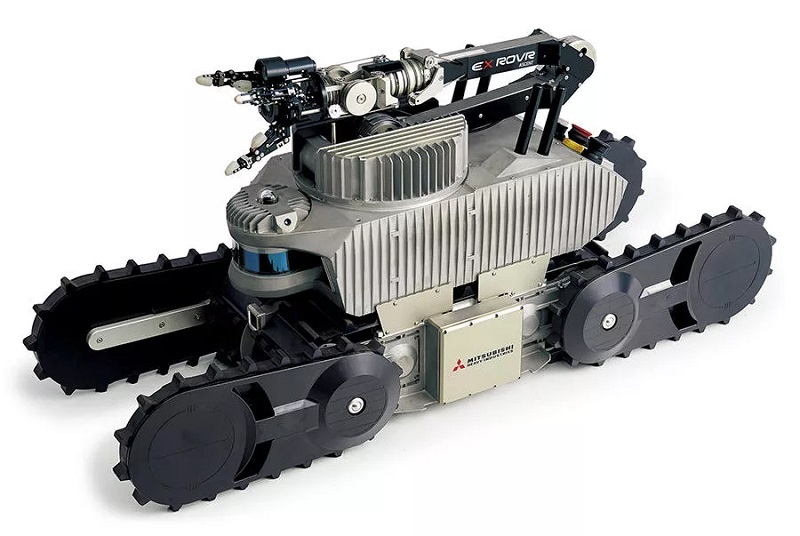
One of the robot options for the OpreX Robot Management Core, the EX ROVR from Mitsubishi. Image used courtesy of Mitsubishi
In these scenarios, it can be beneficial to use robotics to limit the risks to employees, especially in the case of the petroleum industry which can be rife with confined spaces, working at heights, and other hazardous environments. Yokogawa started working with a select few manufacturers in 2019 to develop the technology and has managed to create the latest system through this proof-of-concept methodology.
Features of the OpreX Robot Management Core
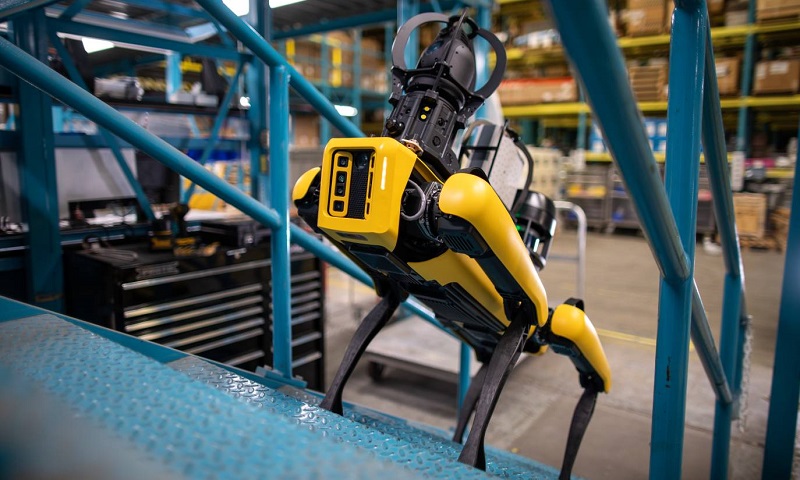
OpreX Robot Management Core features software developed to help with maintenance operations through the use of robotic systems, in either an on-site format or through cloud utilization. The system can operate on either the Spot four-legged robot from Boston Dynamics or the EX ROVR automatic plant patrol, inspection, and explosion prevention robot from Mitsubishi Heavy Industries.
Another one of the robot options for the OpreX Robot Management Core, Spot from Boston Dynamics. Image used courtesy of Boston Dynamics
Remote operation is made possible through a web browser viewer that functions as the software’s management screen. All data collected from the robots can be saved and used later if needed. The robots are capable of collecting images, video, audio, and other data, and can be operated on a scheduled basis or through a manual initiation process.
AI Capable Analysis
The software can replace personnel for many tasks through AI image analysis. One easy-to-integrate use for the OpreX system is replacing manual meter reading and consumable level checking with automated robotics. The robots simply look at the meter or gauge and then record the data for later use and analysis. Yokogawa hopes the technology will boost plant safety through increased accuracy and decreased exposure for workers.
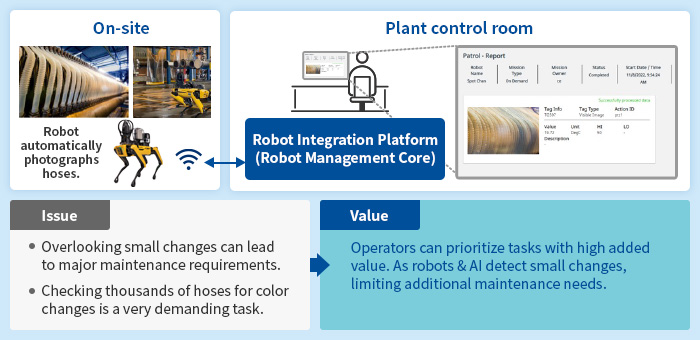
Process flow and problem-solution for robotic inspection and monitoring robotics. Image used courtesy of Yokogawa
The software is compatible with Yokogawa’s OpreX Collaborative Information Server. This ensures that data from the robot can be used with the information from control systems, safety instrumented systems, and integrated asset management systems. As a result, centralized management can start to become a reality for many manufacturers giving them access to not only maintenance management possibilities but operational ones as well.

 Facebook
Facebook Google
Google GitHub
GitHub Linkedin
Linkedin








