
Redundancy and safety are often seen together in industrial safety systems. Safety relays monitor emergency devices to switch contacts based on status - but what…
Redundancy and safety are often seen together in industrial safety systems. Safety relays monitor emergency devices to switch contacts based on status - but what makes them different from normal relays?

Advanced features such as programmable limits, diagnostics, and remote configuration are available with IO-Link devices.…
Advanced features such as programmable limits, diagnostics, and remote configuration are available with IO-Link devices. Learn how to connect an example IO-Link block into an actual PLC project.

Linear position sensors are used in electrical and fluid-actuated motion devices. They allow extremely precise position,…
Linear position sensors are used in electrical and fluid-actuated motion devices. They allow extremely precise position, velocity, and acceleration control, and provide feedback to ensure product quality and tolerance compliance.
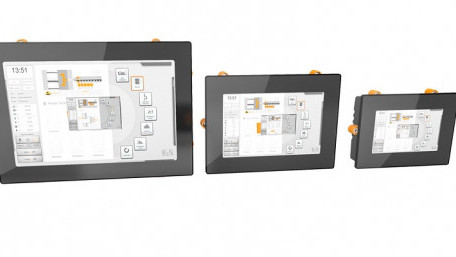
With the increasing appearance of “web-based” HMIs, we investigate these devices, learn how they differ from the…
With the increasing appearance of “web-based” HMIs, we investigate these devices, learn how they differ from the graphical HMIs, and see implications for our modern control system architecture.

AC motors are common throughout industry - easily controlled by VFDs and without the maintenance that comes with DC…
AC motors are common throughout industry - easily controlled by VFDs and without the maintenance that comes with DC brushes. So then, why are DC motors still used in certain applications?

Before digital control systems, responses were fairly slow. Push a button, and a motor contactor engaged. These days, the…
Before digital control systems, responses were fairly slow. Push a button, and a motor contactor engaged. These days, the speed of computers introduces some new challenges but brings solutions as well.

Modbus is a communication protocol stemming from the early days of Modicon PLCs, but is still common today. These two…
Modbus is a communication protocol stemming from the early days of Modicon PLCs, but is still common today. These two example implementations of Modbus transactions will get you started.

Inductive loads, such as solenoids and contactors, can cause arcs and failures back into electromechanical switching…
Inductive loads, such as solenoids and contactors, can cause arcs and failures back into electromechanical switching devices, causing costly downtime. The solution is cheaper than you think.

Failures of I/O systems are a common source of headache for control engineers. Troubleshooting those devices that have…
Failures of I/O systems are a common source of headache for control engineers. Troubleshooting those devices that have polarized connections (source vs sink, and NPN vs PNP) is a technique worth refining.

The fourth pillar of effective statistical process control (SPC) is the use of designed experiments used to learn as much…
The fourth pillar of effective statistical process control (SPC) is the use of designed experiments used to learn as much as possible from a limited number of experiments, yet remain statistically relevant enough to be useful.
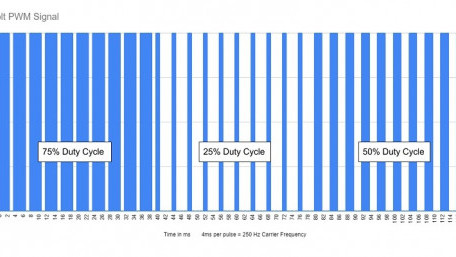
Power delivered to devices can be changed by raising or lowering the voltage and current. But this method does not always…
Power delivered to devices can be changed by raising or lowering the voltage and current. But this method does not always produce intended results. Pulse width modulation (or PWM) can be used to better control variable loads.

Analog and digital multimeters have both enjoyed popularity in different generations of electrical systems. What is…
Analog and digital multimeters have both enjoyed popularity in different generations of electrical systems. What is unique about the analog meters, and in what situations might they be preferred over their digital counterparts?

Statistical process control (SPC) allows for continual improvement process (CIP), a method of optimizing a process driven…
Statistical process control (SPC) allows for continual improvement process (CIP), a method of optimizing a process driven by data and statistical methods.

Learn how control charts are used in statistical process control (SPC) to show how a process changes with time as…
Learn how control charts are used in statistical process control (SPC) to show how a process changes with time as compared to past measurements, providing reliable visualizations for data-driven decisions.

What is a PLC? This article will lay out a succinct definition of a programmable logic controller and explain its basic…
What is a PLC? This article will lay out a succinct definition of a programmable logic controller and explain its basic components.

Pressure and flow rate are terms used in all areas of hydraulic and pneumatic systems. Learn the definition and science…
Pressure and flow rate are terms used in all areas of hydraulic and pneumatic systems. Learn the definition and science of these terms, and the reason they are so important within industry.
Statistical process control (SPC) is meaningless without the proper collection and analysis of data. For some process…
Statistical process control (SPC) is meaningless without the proper collection and analysis of data. For some process parameters, this is a simple task. But not every part of a process is driven by simple, quantitative parameters.
Digital control systems are particular about the direction of current flow from sensors and input devices. The terms…
Digital control systems are particular about the direction of current flow from sensors and input devices. The terms sourcing and sinking (often abbreviated source and sink) are among the more confusing ratings found on I/O module datasheets. Part 1 of a 3-part series.
Any industrial electrician can instantly recognize a relay, but when it comes to wiring, why are the terminals numbered…
Any industrial electrician can instantly recognize a relay, but when it comes to wiring, why are the terminals numbered in such apparently random order?
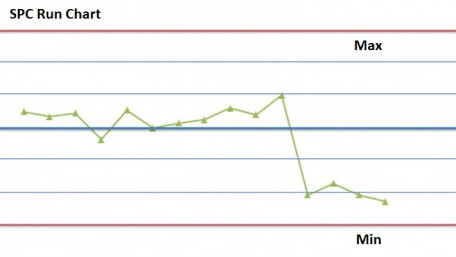
Learn how statistical process control (SPC) can provide a foundation for decisions used to reduce waste and increase…
Learn how statistical process control (SPC) can provide a foundation for decisions used to reduce waste and increase efficiency in the manufacturing process.
