
Power systems rely on meaningful data, as do most other processes. Within SCADA environments, individual data points are tracked, compared to limits, and…
Power systems rely on meaningful data, as do most other processes. Within SCADA environments, individual data points are tracked, compared to limits, and evaluated to obtain current readings.

Rebooting industrial controllers and computers incurs costs, not only from the downtime but also from cascading effects…
Rebooting industrial controllers and computers incurs costs, not only from the downtime but also from cascading effects of communication with up/downstream controllers. How can this downtime be managed?
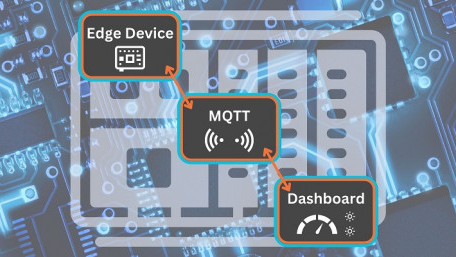
Learn to develop an actual IoT solution end to end. Create a Mosquitto MQTT broker for the Raspberry Pi client in order…
Learn to develop an actual IoT solution end to end. Create a Mosquitto MQTT broker for the Raspberry Pi client in order to connect and publish Sense HAT sensor data.

Learn to develop an actual IoT solution end to end. This second article explains configuration files, testing the edge…
Learn to develop an actual IoT solution end to end. This second article explains configuration files, testing the edge device publisher script, and viewing the payload using a sandbox subscriber script.

Learn to develop an actual IoT solution end to end, from the initial data collection to web-based visualization and…
Learn to develop an actual IoT solution end to end, from the initial data collection to web-based visualization and analytics. This first article in the series will explore the setup of the edge device.

Have you ever needed to know the temperature, pressure, flow, or other measurement on location, but the readout is way…
Have you ever needed to know the temperature, pressure, flow, or other measurement on location, but the readout is way off in the control room? Here’s an easy way to add a readout in the field.

Innovation has a single purpose: to create better solutions, meaning more efficient output with faster development and…
Innovation has a single purpose: to create better solutions, meaning more efficient output with faster development and troubleshooting. It starts with the strategies used to program machines.

Taking web-based HMI design from a simulated project to the real-world environment. Part 1 introduces tag instances and…
Taking web-based HMI design from a simulated project to the real-world environment. Part 1 introduces tag instances and attributes.

A PLC can be placed in Run or Stop, or occasionally Program mode, usually through physical or virtual methods. But what…
A PLC can be placed in Run or Stop, or occasionally Program mode, usually through physical or virtual methods. But what do these modes mean, and when should they be used?

Explore the sensors used to obtain temperature, pressure, and humidity for industrial applications on this value-packed,…
Explore the sensors used to obtain temperature, pressure, and humidity for industrial applications on this value-packed, compact add-on for the Raspberry Pi.

If you’re working collaboratively with teams in a corporate industrial setting and require a version control system for…
If you’re working collaboratively with teams in a corporate industrial setting and require a version control system for critical software or documents, Git is a must-have in your skillset.
Function block diagrams can be a useful tool, but they can also add a lot of complexity. Learn about the what, when,…
Function block diagrams can be a useful tool, but they can also add a lot of complexity. Learn about the what, when, where, and why of function block diagram (FBD) programming.

Some controllers and network devices have one port, while others have two. Why is there a difference, and what advantages…
Some controllers and network devices have one port, while others have two. Why is there a difference, and what advantages does having two network ports actually provide?

This top-mount accessory for the Raspberry Pi offers various capabilities at a low cost, perfect for analyzing and…
This top-mount accessory for the Raspberry Pi offers various capabilities at a low cost, perfect for analyzing and solving problems related to vibration, temperature, humidity, and others.
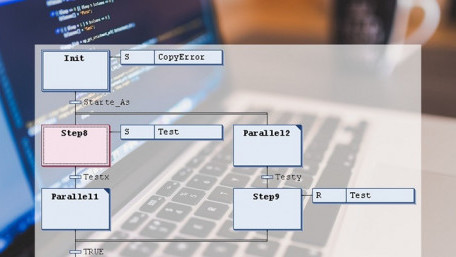
Sequential function charts (SFCs) are a great tool when processes require sequence control, but things can get…
Sequential function charts (SFCs) are a great tool when processes require sequence control, but things can get complicated fast. Here are some ways to create better SFC programs and applications.
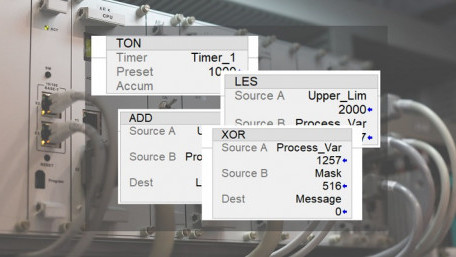
Function block diagram (FBD) programming is a common language for PLCs following the IEC 61131 standard. What is FBD, and…
Function block diagram (FBD) programming is a common language for PLCs following the IEC 61131 standard. What is FBD, and how does it differ from the familiar ladder logic programs?

Analog voltage and current are the dominating standards for industrial technology. Is one format better than the other?…
Analog voltage and current are the dominating standards for industrial technology. Is one format better than the other? And if so, why do both signal types still exist in modern systems?

Automation can be inexpensive for small projects by using development boards. This article presents a walkthrough of the…
Automation can be inexpensive for small projects by using development boards. This article presents a walkthrough of the setup and installation steps for the popular Raspberry Pi.

Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are designed as an endlessly-looping program, examining all lines of code as…
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are designed as an endlessly-looping program, examining all lines of code as rapidly as possible. Following are a few critical tips for when programmers only need to run a series of single operations at startup.

A walkthrough and discussion of a simple web-based HMI solution that could modernize your current HMI technology stack.…
A walkthrough and discussion of a simple web-based HMI solution that could modernize your current HMI technology stack. The first step in the process involves sending data from a device to a server.
