
Industrial sensors can be found in nearly every modern industrial process, regardless of complexity. Learn the history, evolution, and variety of sensors that…
Industrial sensors can be found in nearly every modern industrial process, regardless of complexity. Learn the history, evolution, and variety of sensors that make manufacturing the modern marvel we see today.

Programming simple coil and contact commands is an easy matter in most PLC IDEs. Connecting and configuring analog inputs…
Programming simple coil and contact commands is an easy matter in most PLC IDEs. Connecting and configuring analog inputs can be more challenging with various bit resolutions and conversion commands.
Operating voltage, linearity, dimensions, polarity protection, range… When it comes to sensors, every situation calls…
Operating voltage, linearity, dimensions, polarity protection, range… When it comes to sensors, every situation calls for understanding these specs in detail during design, purchasing, and installation.

To know if predictive maintenance is the right strategy, it might help to first recognize if it isn’t. Here are some…
To know if predictive maintenance is the right strategy, it might help to first recognize if it isn’t. Here are some indicators that your organization should improve before implementing predictive maintenance.

Safety is one of the most critical aspects of machine design. Today, with network connections between different machines…
Safety is one of the most critical aspects of machine design. Today, with network connections between different machines and control centers, safety signals must be shared logically and reliably across networks.

Learn about proportional gain and proportional band, two key proportional control concepts, to better understand the most…
Learn about proportional gain and proportional band, two key proportional control concepts, to better understand the most popular control system method in industrial automation.
You are bound to encounter two terms associated with sensors and some loads: ‘NPN’ and ‘PNP’. You must understand…
You are bound to encounter two terms associated with sensors and some loads: ‘NPN’ and ‘PNP’. You must understand the relationship between the field device and the control module in order to choose and install components properly when needed.

We'll run through the eight basic steps for implementing a predictive maintenance strategy in your business to improve…
We'll run through the eight basic steps for implementing a predictive maintenance strategy in your business to improve critical asset availability, reduced maintenance costs, and enhanced revenues over time.
Industrial analog sensor devices primarily use 0-10 volt or 4-20 milliamp. For those mA signals, learn the reasons for…
Industrial analog sensor devices primarily use 0-10 volt or 4-20 milliamp. For those mA signals, learn the reasons for why the lower and upper limit standards were determined as 4 mA and 20 mA.

Ambient light, reflection, and transparent objects can all cause difficulties during machine vision applications. Learn…
Ambient light, reflection, and transparent objects can all cause difficulties during machine vision applications. Learn about these issues and some potential solutions to better ensure safety and quality.

Learn about the differences between red, green, infrared, and more recently, blue photoelectric sensors and how the…
Learn about the differences between red, green, infrared, and more recently, blue photoelectric sensors and how the different light spectrums can aid in varying industrial automation processes.

What if you could control the end position and the speed of a hydraulic actuator accurately with just a simple signal?…
What if you could control the end position and the speed of a hydraulic actuator accurately with just a simple signal? Some systems use simple open/close valves, but others require far more precision.

Our Control Automation engineering staff got the chance to visit a commercial farm in North Dakota and learn the hardware…
Our Control Automation engineering staff got the chance to visit a commercial farm in North Dakota and learn the hardware and software making these huge automated tractors ready for high-tech ‘field’ work.

Linear position sensors are used in electrical and fluid-actuated motion devices. They allow extremely precise position,…
Linear position sensors are used in electrical and fluid-actuated motion devices. They allow extremely precise position, velocity, and acceleration control, and provide feedback to ensure product quality and tolerance compliance.

Modbus is a communication protocol stemming from the early days of Modicon PLCs, but is still common today. These two…
Modbus is a communication protocol stemming from the early days of Modicon PLCs, but is still common today. These two example implementations of Modbus transactions will get you started.

Moisture inside industrial pneumatic systems is a major cause for concern, and if the air is not filtered or dried…
Moisture inside industrial pneumatic systems is a major cause for concern, and if the air is not filtered or dried properly, it can lead to serious failures.

The fourth pillar of effective statistical process control (SPC) is the use of designed experiments used to learn as much…
The fourth pillar of effective statistical process control (SPC) is the use of designed experiments used to learn as much as possible from a limited number of experiments, yet remain statistically relevant enough to be useful.

Statistical process control (SPC) allows for continual improvement process (CIP), a method of optimizing a process driven…
Statistical process control (SPC) allows for continual improvement process (CIP), a method of optimizing a process driven by data and statistical methods.
Statistical process control (SPC) is meaningless without the proper collection and analysis of data. For some process…
Statistical process control (SPC) is meaningless without the proper collection and analysis of data. For some process parameters, this is a simple task. But not every part of a process is driven by simple, quantitative parameters.
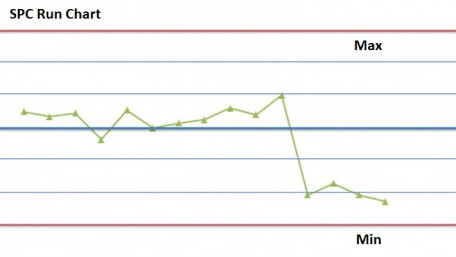
Learn how statistical process control (SPC) can provide a foundation for decisions used to reduce waste and increase…
Learn how statistical process control (SPC) can provide a foundation for decisions used to reduce waste and increase efficiency in the manufacturing process.
