
Computers understand values as long strings of binary bits, but we humans convert them to other systems for convenience. Decimal makes sense, but what about…
Computers understand values as long strings of binary bits, but we humans convert them to other systems for convenience. Decimal makes sense, but what about hexadecimal and the lesser-known octal systems?
Operating voltage, linearity, dimensions, polarity protection, range… When it comes to sensors, every situation calls…
Operating voltage, linearity, dimensions, polarity protection, range… When it comes to sensors, every situation calls for understanding these specs in detail during design, purchasing, and installation.
This article discusses the meaning and effects of proportional gain in a controlled system such as motion, temperature,…
This article discusses the meaning and effects of proportional gain in a controlled system such as motion, temperature, and fluid flow.

To know if predictive maintenance is the right strategy, it might help to first recognize if it isn’t. Here are some…
To know if predictive maintenance is the right strategy, it might help to first recognize if it isn’t. Here are some indicators that your organization should improve before implementing predictive maintenance.

Actuators are used to control the motion of manufacturing devices and raw materials. This article will compare electric…
Actuators are used to control the motion of manufacturing devices and raw materials. This article will compare electric actuators and several types of fluid-power actuators.

Closed-loop motor control is a control system used to regulate the output of a motor. Learn about the four common types…
Closed-loop motor control is a control system used to regulate the output of a motor. Learn about the four common types of closed-loop motor control systems to understand each one’s inner-workings and applications.

Programming robots may seem like a simple task of moving from point to point, like a really expensive game of Connect the…
Programming robots may seem like a simple task of moving from point to point, like a really expensive game of Connect the Dots. Linear, joint, and circular motion commands affect robot movement differently, each meant to be used in certain settings.

Total laboratory automation (TLA) helps in workforce utilization, reduced costs, and management of routine testing. Learn…
Total laboratory automation (TLA) helps in workforce utilization, reduced costs, and management of routine testing. Learn about what TLA is, its components, and what to consider before replacing a traditional laboratory.

Using advanced sensing technology, robotic skin allows grippers and manipulators to “feel” and handle objects without…
Using advanced sensing technology, robotic skin allows grippers and manipulators to “feel” and handle objects without damaging them. While emulating human touch is still in its infancy, it does show promise for future applications.

There are three main types of numeric values that must be handled by a PLC: boolean, integers, and floating point. These…
There are three main types of numeric values that must be handled by a PLC: boolean, integers, and floating point. These last floating-point values can create the most confusion for programmers and technicians.

Tracking the position of a hydraulic or pneumatic cylinder is often accomplished at a basic precision level, detecting…
Tracking the position of a hydraulic or pneumatic cylinder is often accomplished at a basic precision level, detecting only end stop limits with discrete digital values… But what methods accomplish this?
You are bound to encounter two terms associated with sensors and some loads: ‘NPN’ and ‘PNP’. You must understand…
You are bound to encounter two terms associated with sensors and some loads: ‘NPN’ and ‘PNP’. You must understand the relationship between the field device and the control module in order to choose and install components properly when needed.
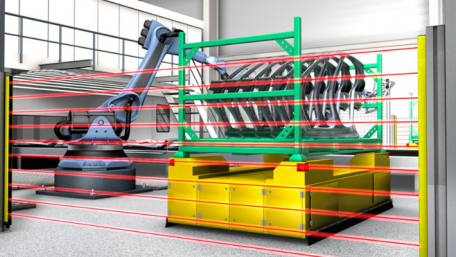
Light curtains serve as an invisible barrier, keeping workers out of harm's way and protecting machinery from damage.…
Light curtains serve as an invisible barrier, keeping workers out of harm's way and protecting machinery from damage. Learn about safety curtains, how they are installed, and their programmable functions.
Industrial analog sensor devices primarily use 0-10 volt or 4-20 milliamp. For those mA signals, learn the reasons for…
Industrial analog sensor devices primarily use 0-10 volt or 4-20 milliamp. For those mA signals, learn the reasons for why the lower and upper limit standards were determined as 4 mA and 20 mA.

Raspberry Pi is a low-cost, educational single-board computer platform with the potential for industrial applications. In…
Raspberry Pi is a low-cost, educational single-board computer platform with the potential for industrial applications. In this article, we discuss the purpose of Raspberry Pi as well as its hardware and software.

Humidity control is vital in many industrial applications. We'll take a look at nine different humidity measurement…
Humidity control is vital in many industrial applications. We'll take a look at nine different humidity measurement technologies, how they are used, and discuss the difference between relative humidity and dew point.
An EOAT, located at the end of an industrial or collaborative robot arm, is entirely customizable with nearly unlimited…
An EOAT, located at the end of an industrial or collaborative robot arm, is entirely customizable with nearly unlimited possibilities. Learn about the five main methods of how EOATs are powered and the sensors that they use.

All real-time power system data can be communicated to a central control system to protect main equipment from…
All real-time power system data can be communicated to a central control system to protect main equipment from overloading. Learn how to create a project directory structure, hardware configuration, and set network tree parameters for real-time control and monitoring.

Remote locations are notoriously difficult to supply power, yet they are the exact locations where many data points must…
Remote locations are notoriously difficult to supply power, yet they are the exact locations where many data points must be collected. How can IoT devices be designed to conserve power to last for months or even years?

Learn about the four IIoT architecture layers: perception, network, processing, and application, and how these layers…
Learn about the four IIoT architecture layers: perception, network, processing, and application, and how these layers are necessary to implement IIoT in an industrial setting to benefit varying processes.
