Instruments and Solutions for Automatic Boiler Control
Explore the importance and solutions for automated boiler system controls that help to increase performance and efficiency.
The boiler system is the combination of different components and instrumentation used to monitor the boiler’s performance following the user requirements. It also serves to enhance the boiler’s working in different scenarios and conditions. Boiler systems can be customized to perform many functions depending upon the size, capacity, area of application, and industry.

Figure 1. Boiler systems are highly customizable, enabling them to work in different environments. Image courtesy of Siemens.
A boiler is one of the critical components in a variety of industrial processes because they are the main source of heat. Different types of energy generation are performed with the help of steam. Among all of the systems and elements of a boiler, the control system is crucial as they directly command the boiler working. The system not only provides the operational mechanism for the boiler, but it also paves the way for synchronizing the boiler with the changing load requirements throughout the product lifecycle.
Importance of Monitoring
The installation of a boiler in any factory is considered to be a key investment in factory advancement. Aside from the financial investment, the boiler’s selection takes time and involves a considerable amount of planning and implementation challenges. In order to secure these efforts, boilers are equipped with performance monitoring systems to stop the boiler from falling below the required performance levels.
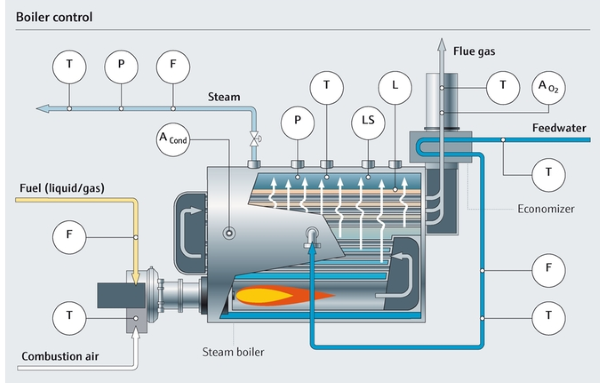
Figure 2. There are many parts of a boiler that benefit from consistent system monitoring. Image courtesy of Endress + Hauser.
Nowadays, manufacturers pay special attention to establishing monitoring systems. Monitoring helps to improve the boiler’s performance and provides insight in the case of any problems.
Some reasons for using boiler monitoring systems are:
- Maximizing efficiency
- Safer operation
- Availability of data for analytics
Maximizing Efficiency
By continuously measuring exhaust emissions concentration, operators can predict what’s going inside the boiler. The abnormal exhaust emission of gasses is a sign of a fuel combustion problem. By detecting aberrant emission of certain gasses, the maintenance team has information for more immediate corrective actions in place. This also prevents the boiler from tedious and excessive shutdown as a result of a problem.
Safer Operation
Monitoring greatly increases the boiler’s safety. The boiler is a giant steam container running at high pressures. If not effectively managed, it can become dangerous. There can be many reasons for malfunctions, including human error, attached piping fault, or defective installation. Correct monitoring allows detection of problems in their initial stage, enabling prompt action before it becomes an emergency.
Availability of Data for Analytics
Performance monitoring enables the collection of critical data for condition monitoring, as the collection of relevant data is the first step in implementing a condition monitoring program.
Solutions to Help Streamline a Boiler
After electricity, steam is the most common basic requirement of many industries because it fulfills most of the heating requirements. Considering steam’s vital role, industry owners and managers are under constant pressure to optimize the boiler’s performance. Due to rising energy costs, a boiler is not an easily replaceable equipment asset.
To avoid performance mismatch and degraded efficiency the following efforts can contribute towards up to the mark performing boiler:
- Feedwater treatment
- Fuel Combustion
- Steam flow
- Exhaust gas
Feedwater Treatment
The quality of feedwater to the boiler affects the quality of steam and has a great impact on boiler performance. Water contains different materials and minerals. If not correctly separated, these particles can affect the boiler with problems such as corrosion and scaling of the inside structure. Improperly filtered water could lead to long downtime and expensive maintenance.
The water treatment system deploys to avoid the problems caused by contaminated feedwater, which effectively removes material that is harmful to the boiler. Feedwater first goes into the purification treatment system, making it useable for the boiler. Most commonly, the treatment system process includes:
- Filtration
- Ion exchange
- Membrane
- Chemical treatment
Fuel Combustion
The combustion of fuel has a direct impact on the boiler’s life and performance. If the fuel is not fully combusting, it’s not all burning, meaning some proportion of it is being wasted through the exhaust. This results in wastage of fuel and violates the emissions standards of the regulatory body.
Having fuel combustion methods allows for optimal fuel burning. The fuel does not remain un-burnt and emissions stay under control.
Steam Flow
Monitoring the boiler output provides important facts about the boiler’s overall performance. Measuring the quality of steam — i.e., the ratio of condensate in the steam and the temperature — provides useful information about the internal working efficiency. It also gives feedback on whether the boiler is working according to its rated capacity.
The results of these measurements are sent back to the controller as feedback to adjust the control boiler’s different functions to have a maximum outcome at the maximum efficiency.
Exhaust Gas
In today’s industrial world, every market pays special attention to environmental protection and almost all markets have regulatory bodies monitoring their pollution. If a particular industry does not comply with the environmental standards, then the respective regulatory bodies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States take serious action against these factories. Further violation of these standards can cause the relevant body to shut down the industry until necessary compliances are made.
The monitoring of exhaust gas enables operators to keep track of different boiler functions by measuring different gasses and their levels in the exhaust. It also helps to keep the boiler’s operation in accordance with respective regulatory bodies.

 Facebook
Facebook Google
Google GitHub
GitHub Linkedin
Linkedin








